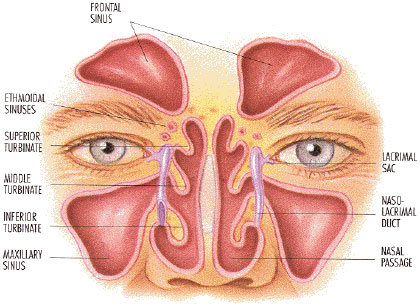
The paranasal sinuses are typically the seat of acute or continual irritation. Anatomical abnormalities interfering with the normal draining mechanisms predispose to infection. Infection reaches the sinuses from the nose, mouth, tonsils, nasopharynx, and the upper canines or molars. The bacterial flora are typically mixed, which includes streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, Klebsiella, E.Coli and anaerobes. The lining mucosa is inflamed and the sinus could be filled with pus.
Medical functions Acute sinusitis begins with headaches, fever, rigor and chills. Tenderness might be elicited over the sinuses. Pus might be witnessed pouring from the opening of the impacted sinus on speculum examination. The issue tends to turn into persistent if not appropriately taken care of.
Continual sinusitis prospects to recurrent headache, which demonstrates a diurnal periodicity- the headache starting up in the morning and worsening by mid-day, to subside by evening. Foul- smelling purulent nasal discharge could arise. After established, the issue persists for months or even many years. Infection may possibly spread to trigger meningitis, thrombophlebitis of the intracranial veins, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus and sagittal sinus, and extradural abscesses. Aspiration of pus into the respiratory tract prospects to recurrent bronchitis, aspiration pneumonia, bronchiectasis, and lung abscess. Infection of the ethmoid sinus may possibly cause 3rd nerve palsy or spread to the orbit to generate orbital cellulites and unpleasant exophthalmos. Frontal sinusitis may possibly result in osteomyelitis of the frontal bone and edema over this area (Pott's puffy turmor).
Diagnosis Sinusitis ought to be suspected from the background of persistent headache and the demonstration of purulent discharge from the nose. X-ray examination of the skull displays opacity over the impacted sinuses.
Therapy Particular Treatment method is to administer antibiotics based on bacteriological outcomes. In the acute stage, penicillin is efficient in typical dosage. Decongestant nasal drops and steam inhalations assist in decreasing nasal mucosal edema and therefore favor drainage of pus. Aspirin provides symptomatic relief. In continual sinusitis, if conservative measures fail to distinct the infection, pus has to be eliminated by puncture and wash out.
0 comments:
Post a Comment